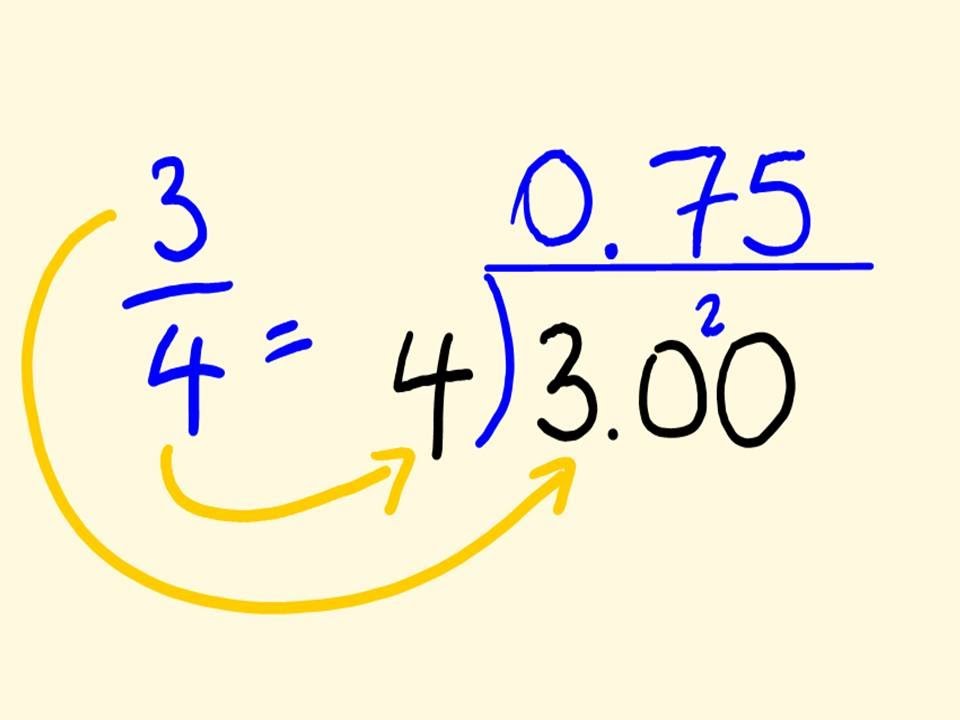Smart Ways to Convert a Fraction to a Decimal in 2025
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
To effectively learn how to convert fractions to decimals, it’s essential to grasp both concepts. A fraction represents a part of a whole, while a decimal is a way of expressing a fraction whose denominator is a power of ten. By understanding decimals, you enhance your capability in mathematical calculations, enabling better engagement with **mathematical literacy**. This foundation allows you to visualize fractions which is critical for mastering techniques like decimal conversion methods and understanding their relationships with percentages.
Types of Fractions
Fractions fall into various categories, primarily **proper, improper**, and **mixed numbers**. Understanding these types is crucial for accurate conversions. Proper fractions have numerators smaller than denominators (e.g., 1/2), while improper fractions have larger numerators (e.g., 5/3). In contrast, mixed numbers combine whole numbers and fractions (e.g., 1 1/2). For instance, converting the mixed number 1 1/2 to a decimal involves transforming it first to an improper fraction (3/2) and then into decimal form, resulting in 1.5. Such examples demonstrate the frequent nature of fractions in real life, from recipes to finances.
Decimal Notation Explained
**Decimal notation** provides a way to display decimal equivalents of fractions by using a decimal point to separate whole numbers from fractional parts. For instance, the fraction 3/4 converts to 0.75 in decimal form, indicating that in terms of fractional value, you have three parts out of four. This transition is essential in many applications, such as calculations in banking and engineering, especially in dealing with significant figures in decimals that add precision to measurements.
Methods for Convert Fraction to Decimal
Mastering how to convert fractions to decimals involves several methods, each useful under different circumstances. The most common techniques include the **long division method**, using calculators, and fraction simplification. Identifying which method works best for you can enhance your math skills, making calculations more efficient and intuitive.
Long Division Method
The **long division method** is a classic approach to converting fractions into decimals, primarily effective for both proper and improper fractions. To apply this method, divide the numerator by the denominator. For example, to convert 3/4: divide 3 by 4. The result is that 4 goes into 3 zero times, hence placing a decimal point and adding a zero to continue. Continuing with 30, we find that 4 goes into 30 seven times (28), yielding a decimal value of 0.75. This iterative technique builds a foundational understanding of **dividing numerators** effectively in division in math.
Using Calculators
For those looking to simplify their calculations, using calculators is an efficient technique. Most scientific calculators have a simple function for converting fractions into their decimal equivalents. Whether you input fractions directly or utilize a fraction-to-decimal converter found online, this tool is crucial for facilitating complex mathematical calculations. By **using calculators**, students can focus on understanding how to **calculate decimals**, as the tech handles the conversion process seamlessly.
Practical Applications of Decimal Representation
Understanding how to convert fractions into decimals has practical applications in everyday life, enhancing your capacity for effective decision-making in contexts like finance, cooking, and budgeting. This knowledge empowers individuals to communicate numerical information accurately and effortlessly, making it relevant across various domains.
Everyday Decimal Uses
In practical scenarios, decimal representation simplifies complex data interpretation. For example, consider a recipe that calls for 3/4 cup of sugar. To simplify measuring in everyday cooking, converting that fraction into decimal would yield 0.75 cups, helping to align with modern measuring tools. Mastering such **everyday decimal uses** ensures that fractions remain relatable and applicable.
Understanding Percentages
Converting fractions to decimals also leads to a deeper understanding of percentages, as both concepts intersect routinely. For instance, when expressing 1/4 as a decimal (0.25), you can succinctly convert it into a percentage (25%). This unique connection helps to simplify matters, making concepts clearer and quantifiable, especially useful in **comparing fractions and decimals** across diverse mathematical problems.
Challenges and Strategies in Fraction to Decimal Conversion
While converting fractions to decimals may appear straightforward, many learners face challenges throughout this process. Some common hurdles include confusing techniques, misplacement of decimal points, and failure to recognize repeating decimals. Implementing strategic approaches can bridge these challenges, enhancing knowledge retention and practical application.
Decimal Point Placement Techniques
**Decimal point placement** is an essential skill when converting fractions to decimals, as small inaccuracies can lead to significant mathematical errors. Ensuring that decimal points are accurately positioned is vital in maintaining the integrity of a mathematical expression. For example, recognizing that 1/3 converts to a repeating decimal (0.333…) helps visualize and recalls crucial decimal fraction characteristics.
Rounding Decimals for Clarity
Another practical challenge arises in **rounding decimals** accurately. It is often useful when working with non-terminating decimals, where practical approximations improve comprehension without losing significant accuracy. Knowledge of where to round, along with the significance of digits, provides clarity, especially when assessing data and communicating numerical evidence.
FAQ
1. How do I simplify a fraction before converting it to a decimal?
Simplifying fractions involves dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their greatest common divisor. This gradually results in the simplest form, making conversion easier. For example, simplifying the fraction 8/12 to 2/3 can help produce a more manageable decimal, specifically 0.666… when divided.
2. What is the best technique for converting mixed numbers?
To convert mixed numbers to decimals, change the mixed fraction into an improper fraction. For instance, to convert 1 1/4, change it to 5/4. Dividing 5 by 4 gives you 1.25. This two-step method guarantees accuracy and ease in calculations!
3. Can I convert fractions with repeating decimals?
Yes, fractions like 1/3 yield repeating decimals (0.333…). It’s commonly recognized and easily calculated. Identifying fractions produced as repeating decimals is fundamental in understanding their applications across percentages and decimal representations.
4. Are there online tools for converting fractions to decimals?
Absolutely! Several **online fraction converter** tools can efficiently perform conversions. Input your fraction, and the tool immediately provides you with the decimal equivalent, saving time and effort in calculations.
5. What role do decimals play in real-life applications?
Decimals significantly help in real-life scenarios, especially in finance, measurements, and statistics. Understanding proportions, calculating percentages, and making financial predictions all rely heavily on decimal comprehension. By mastering conversion techniques, individuals gain crucial skills for accurate assessments and decision-making.
6. How does visualizing fractions aid in learning?
Utilizing **visual fraction tools** enables clearer interpretation of concepts. By associating fractions with visual aids, learners enhance their ability to understand decimal relationships and comparative contexts effectively.
7. What types of fractions are common in everyday calculations?
**Common types of fractions** include proper, improper, and unit fractions. Each has utility in daily mathematical calculations—from cooking to budget management, ensuring fractions remain relevant in personal finance operations.