How to Read an EKG: Effective Techniques for 2025
Reading an EKG (electrocardiogram) can feel daunting at first. With the increase in technology and understanding of heart physiology, mastering the art of EKG interpretation is essential for healthcare professionals. This article will guide you through the essentials of **how to read an EKG**, focusing on understanding heart rhythms and interpreting **electrical heartbeat** signals. By effectively learning these techniques, you will be better equipped to identify **normal EKG findings**, **abnormal EKG patterns**, and more, ensuring better patient assessment and improved heart health monitoring.
EKG Basics: Understanding the Landscape of Heart Rhythms
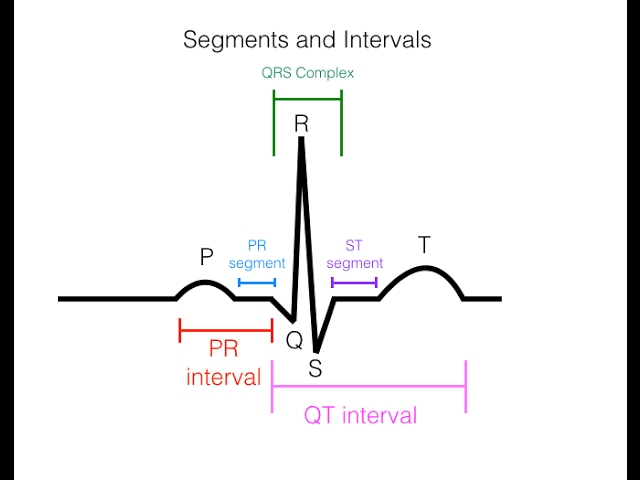
The first step in effective EKG reading is to familiarize yourself with the key elements of an EKG trace. An EKG represents the electrical activity of the heart over a set period. To understand **EKG interpretation**, grasp the waveform characteristics: the **P wave**, **QRS complex**, and **T wave**. Each component has distinct features and significance in cardiac functioning. The **P wave** signifies atrial depolarization, while the **QRS complex** reflects ventricular depolarization, and the **T wave** marks ventricular repolarization. By mastering these components, you can establish a foundation in **heart rhythm analysis**.
Components of the EKG Trace
When analyzing an EKG, it’s crucial to understand what each wave represents. The **P wave** often appears as a small, rounded wave preceding the **QRS complex**. A normal **QRS complex** is sharp and narrow, usually lasting less than 0.12 seconds. The **T wave** follows and is typically asymmetrical and rounded. Detecting abnormalities within these waves can reveal key insights into **cardiac conditions** and disturbances. For instance, a prominent **P wave** could indicate atrial enlargement, while a prolonged **QRS complex** may suggest issues with ventricular conduction.
Heart Rate Calculation Techniques
Understanding heart rate is paramount when interpreting an EKG. To calculate the heart rate from an EKG strip, one common technique is to use the “300 rule.” Count the number of large squares between two consecutive **R waves** in the **QRS complex** and divide 300 by that number. For example, if there are three large squares, then the heart rate is 100 beats per minute. This straightforward method emphasizes speed and proficiency in **cardiac monitoring** practices, allowing healthcare providers to swiftly assess **heart rate and rhythm abnormalities**.
Advanced EKG Interpretation: Identifying Abnormal Patterns
As professionals become more familiar with EKG readings, recognizing **abnormal EKG patterns** becomes invaluable for clinical decision-making. Conditions such as arrhythmias or myocardial infarction can significantly alter EKG appearances. For instance, **ventricular tachycardia** will show wide, abnormal **QRS complexes** that may lead to hemodynamic instability. Diagnosing these issues accurately requires continuous practice and updated knowledge of **electrophysiology**.
Arrhythmia Detection Strategies
Arrhythmia detection is a critical aspect of EKG analysis. Healthcare providers need to look for irregularities in the R-R interval, which is the distance between successive R waves. A consistent R-R interval generally suggests a regular rhythm, while varying intervals may indicate junctional or atrial fibrillation. Using specialized EKG software can enhance the ability to identify these heart rhythm disorders. Familiarity with how to detect arrhythmias plays a crucial role in **cardiac diagnostics** and patient care.
Case Study: Analyzing a Complex EKG Strip
Consider an EKG strip that presents irregular R-R intervals interspersed with occasional **premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)**. Such a strip signifies that the heart attempts to realign its rhythm but experiences disruptions. A case like this underscores the necessity for detailed **EKG strip analysis** and **clinical guidelines** when diagnosing and treating patients. Employing telemetry monitoring can help keep a continuous watch on rhythm abnormalities, giving comprehensive data for further evaluation.
Current Trends in EKG Technology
In 2025, advances in EKG technology offer unprecedented capabilities for heart health assessment. Traditional EKG machines are now complemented by digital health solutions such as wearable ECG monitors and telemedicine applications, allowing for continuous monitoring and easy access to heart health data. The role of **patient education** in this evolving landscape is crucial; understanding how to use such devices effectively enhances patient safety and aids in timely interventions.
Integrating Wearable ECG Monitors
Wearable devices have revolutionized **cardiac monitoring** by enabling real-time data capture. These devices can alert patients of potential issues, facilitating early intervention strategies. For example, a smartwatch displaying irregular heart rhythms can prompt the user to consult their healthcare provider immediately, which is crucial in preventing acute cardiac events. Emphasizing the adoption and integration of these technologies into routine cardiovascular assessments ensures that healthcare providers stay ahead in managing their patients’ heart health.
Telemedicine Applications in Cardiology
Telemedicine has emerged as a powerful tool in **cardiac care**, replacing traditional limitations with enhanced outreach. A growing number of patients can access cardiology services remotely, making it easier for healthcare providers to monitor their patient’s heart health continuously. Video consultations enable thorough evaluations, where both parties engage in discussions about symptoms and EKG readings. Implementing **telehealth practices in cardiology** fosters better engagement and management of patients, ultimately improving adherence to prescribed treatment plans.
Conclusion
Mastering **how to read an EKG** is fundamental for any healthcare provider working within cardiology. Continuous education and adapting to new technologies will enhance skills, ensuring accurate patient assessments of cardiac rhythms. Learning effective **EKG interpretation** techniques — from recognizing waveform characteristics to utilizing advanced tools for monitoring — allows you to provide timely and effective interventions for better patient outcomes. As you continue practicing these skills, remember that constant learning and engagement with new advancements will significantly improve your competence in heart rhythm analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the key components of EKGs: P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
- Recognize abnormal EKG patterns such as arrhythmias and myocardial infarctions.
- Leverage technology tools like wearable ECG monitors and telemedicine for better cardiac assessment.
- Continuous education in EKG practices is essential for improving patient outcomes.
FAQ
1. What should I focus on first when learning EKG interpretation?
Begin by mastering the basic components of an EKG, focusing on the **P wave**, **QRS complex**, and **T wave**. Understanding these elements will provide a solid foundation for identifying **normal EKG findings** and detecting common **arrhythmias**.
2. How can technology enhance EKG readings?
Technology such as **telemedicine applications** and **wearable ECG monitors** enhances EKG readings by providing real-time data and facilitating remote monitoring. This allows healthcare providers to respond quickly to monitoring alerts and improves overall patient engagement in heart health assessments.
3. What are some common arrhythmias to identify on an EKG?
Common arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and premature ventricular contractions (PVCs). Key indicators can be found in the **R-R interval** and the morphology of the **QRS complexes**.
4. How can I calculate heart rate from an EKG?
To calculate heart rate, use the “300 rule” by counting the number of large squares between R waves in the **QRS complex** and dividing 300 by that number. This quick strategy assists in efficient **EKG interpretation** during clinical assessments.
5. What role does continuous monitoring play in cardiac care?
Continuous monitoring is crucial for detecting **electrical heartbeat** modifications and potential **cardiac events** in patients. It enables timely interventions and enhances patient safety, especially in acute care settings.