Effective Ways to Find Percent Yield in 2025
Understanding Percent Yield in Chemistry
The concept of **percent yield** is essential in chemical experiments, providing insights into the efficiency of reactions. In simple terms, % yield measures the ratio of the **actual yield** to the **theoretical yield**, multiplied by 100. Mathematically, it is expressed through the **percent yield formula**: Percent Yield (%) = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100. Understanding this formula is crucial for assessing how well a chemical reaction proceeds toward its expected results. Whether in academic laboratories or industrial processes, being able to determine the **percent yield** enables chemists and researchers to evaluate the performance of their synthesis and improve outcomes in future experiments. Various factors can affect the yield, and analyzing these can provide further understanding of the **percent yield significance** in any experiment.
Defining Percent Yield
Before delving into calculations, it’s important to establish a clear **percent yield definition**. Percent yield is a key metric in the world of chemistry, as it reflects the efficiency of reactions under varying conditions. Typically, the **theoretical percent yield** is the maximum amount you expect to produce based on stoichiometric calculations. However, the **experimental percent yield** is what one actually obtains from the reaction. The discrepancy between these two values can sometimes lead to a **low percent yield**, indicating issues such as incomplete reactions, side reactions, or losses during the product isolation phase. Knowing how to effectively calculate the **percent yield percentage** helps chemists identify these problems and takes steps to enhance the process.
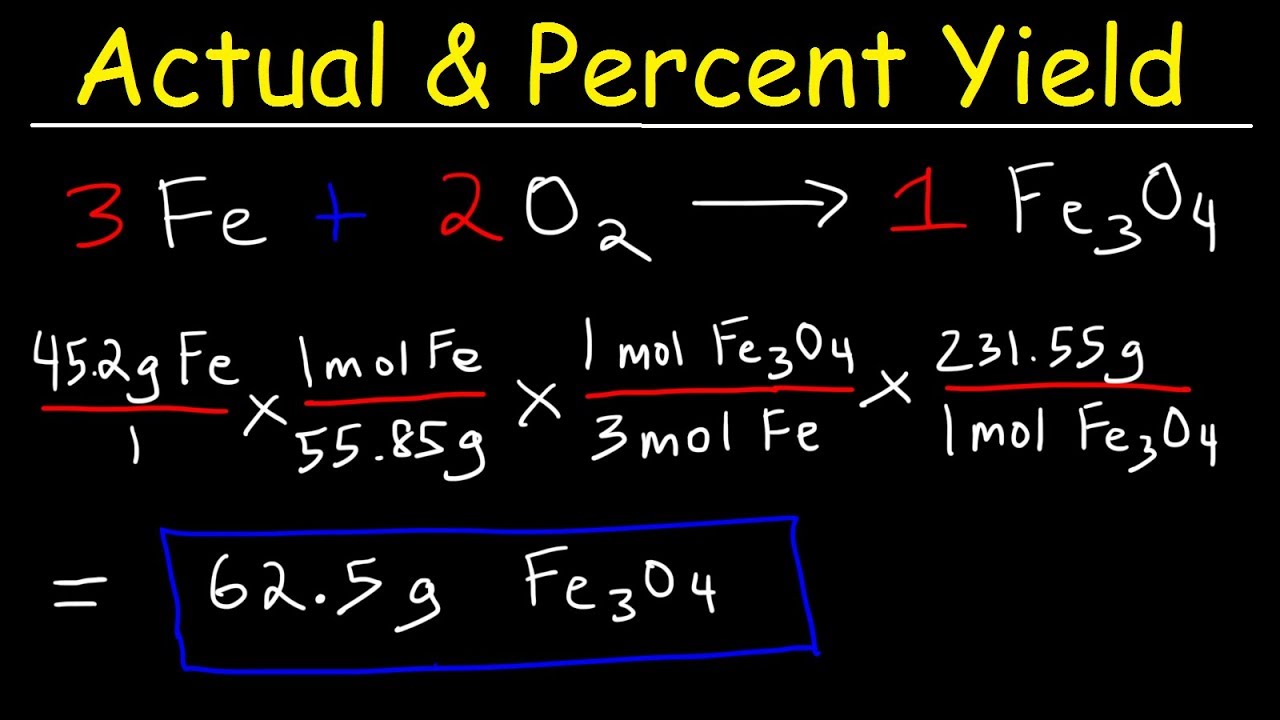
Calculating Percent Yield: A Step-by-Step Guide
To effectively **calculate percent yield**, one must follow a series of logical steps that ensure accuracy. Below is a simple guide:
- Determine the Theoretical Yield: Calculate the expected yield using stoichiometric ratios based on balanced equations.
- Measure the Actual Yield: After conducting the experiment, determine the amount of product obtained.
- Apply the Percent Yield Formula: Use the formula: Percent Yield (%) = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100.
By adhering to these steps for **percent yield calculation**, you can ensure a robust analysis of the reaction’s effectiveness.
Factors Affecting Percent Yield
Factors affecting percent yield range from the purity of reactants to the reaction’s conditions. Many varying elements come into play when a reaction doesn’t yield the expected outcome. Understanding these factors allows for adjustments to be made, ultimately striving for a **high percent yield** in future experiments.
Reagents and Their Purity
The **purity of reagents** drastically impacts overall yield. Impurities can lead to by-products or incomplete reactions, resulting in a **low percent yield**. To mitigate this issue, chemists should always seek high-purity reactants and frequently conduct purity tests prior to proceeding with synthesization. Implementing rigorous reagent selection is a fundamental step in pursuing better yield results.
Reaction Conditions and Their Role
The conditions under which a reaction proceeds, such as temperature and pressure, play a pivotal role in determining the final yield. Optimizing these conditions to suit specific reactions can drastically improve the **percent yield in experiments**. For instance, certain reactions may yield higher products when maintained at elevated temperatures. Experimentation with such variables is critical for achieving maximum reaction efficiency.
The Importance of Accurate Measurements
Finally, **measuring yields accurately** is crucial in any lab setting. Device calibration, meticulous weighing, and diligent recording are all necessary practices. Even small errors can lead to significant discrepancies in yield calculations. By ensuring precise measurements, one can achieve a more reliable understanding of performance and the resulting **percent yield analysis**.
Improving Percent Yield for Chemical Reactions
Pursuing a **high percent yield** involves continuous improvement through many strategies. By implementing a series of best practices, chemists can significantly enhance their yield outcomes. This exploration into yield optimization stands critical to maximizing productivity across laboratory settings and industrial practices.
Modification of Reaction Conditions
One effective way to improve yield is through adjusting **reaction conditions**. As previously mentioned, altering factors like temperature and pressure directly impacts yield. Chemists often conduct preliminary experiments to identify the ideal parameters for their reactions, aiming to create conditions that favor the desired products while minimizing potential side reactions or losses.
Utilizing Advanced Techniques
Employing modern methodologies, such as continuous flow chemistry, can lead to improved results. These techniques allow the reaction to be controlled more accurately, leading to **higher experimental percent yield** by optimizing mixing and heat transfer rates during the reaction. Research into these areas is revolutionizing the concept of yield optimization in chemistry.
Regular Yield Monitoring and Data Analysis
Finally, making a habit of regularly monitoring yield and performing **statistical yield analysis** can lead to significant performance gains. By capturing data and understanding historical yield trends, researchers can make informed adjustments to their methodologies, leading not only to greater lab efficiencies but also reliable applications in real-world scenarios.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding **percent yield** is vital for evaluating chemical efficiency.
- Accurate calculations help in identifying areas for improvement in yield.
- Upon carefully analyzing **factors affecting percent yield**, chemists can improve conditions and reactivity.
- Utilizing advanced techniques could propel yield optimization in experimental settings.
- Regular assessments and adjustments are essential for achieving consistent high performance in laboratory experiments.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between theoretical yield and actual yield?
Theoretical yield refers to the maximum amount of product expected from a reaction, based on stoichiometric calculations. In contrast, **actual yield** is the quantity of product actually produced in an experiment. Understanding this distinction is essential for calculating **percent yield** accurately.
2. How can I improve my percent yield in experiments?
To improve your **percent yield**, optimize reaction conditions, use high-purity reagents, and ensure precise measurements. Experimenting with different parameters may yield improvements, alongside employing advanced techniques such as continuous flow reactions.
3. Why is percent yield significant in organic chemistry?
In organic chemistry, **percent yield** provides insight into the efficiency and practicality of synthesis methods. High yields demonstrate successful reactions, while low yields highlight problems that may need addressing, thus reinforcing the importance of yield in chemical development.
4. What are the common causes of low percent yield?
Common causes of **low percent yield** include incomplete reactions, losses during purification or filtration, and side reactions that produce unwanted by-products. Identifying these issues enables chemists to enhance their processes.
5. Is there a standard percent yield that is considered acceptable?
There is no universally accepted “acceptable” **percent yield**, as it greatly depends on the particular chemical process and goals of the experiment. However, consistently achieving yields above 70% is generally considered good in many scenarios.